What is Varicocele?
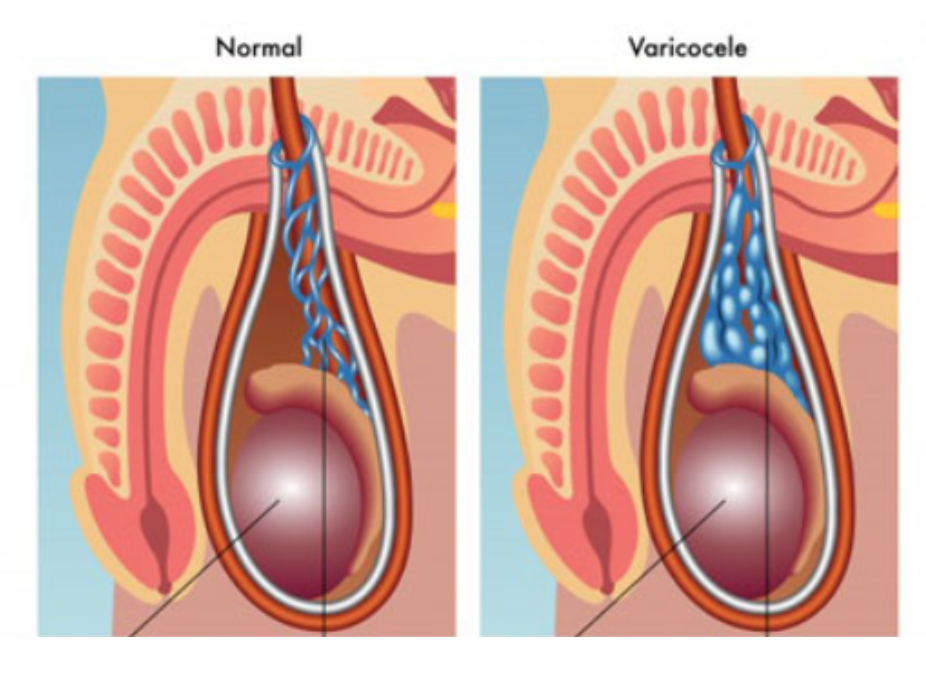
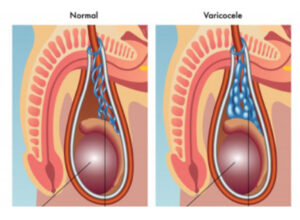
Varicocele is the varicose veins that drain the blood in the testicles, which is seen in approximately 30-40% of those who apply to the doctor with the problem of infertility. Varicocele is the clinical name given to the varicose-like enlargement of the testicular veins in the legs. Deterioration of testicular temperature affects testicular functions and impairs sperm and testosterone production by accumulation of toxic substances in dirty blood in the testis and disrupting testicular blood flow.
What are the Symptoms ?
Varicocele symptoms are very important for the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Varicocele on testis;
- Swelling
- Fluffiness
- It may give symptoms in the form of pain in the testis.
The enlargement of the veins may become so obvious that it can be seen from the outside after a while and take a form similar to varicose seen in the legs. Varicocele symptoms include swelling in the testicles, as well as sweating and a feeling of warmth. Although rare, shrinkage of the testicles, which is one of the symptoms of varicocele, can be seen in some patients.
What Causes Varicocele?
The cause of varicocele is unknown. It is seen in 15-20% of individuals who have children in the society, even at adult ages. It is observed at a rate of 30-40% in men who apply due to infertility. Secondary infertility, that is, in those who have had a child before and apply with a request for a child again, this rate can reach up to 60%.
While varicocele is seen in 90% left testis, it is observed bilaterally (bilaterally) in 8-9%. The rate of being seen only on the right side is 1-2%. The fact that varicocele is mostly seen on the left side depends on a number of anatomical factors.
- The testicle on the left is slightly lower than the one on the right.
- The vein on the left side of the testis is longer than the right side.
- Anatomical relationship of the left testicular vein with other adjacent organs in the abdomen.
- Among the features such as the anatomical structure of the discharge of the left-sided testicular vein, varicocele is mostly seen on the left side.
How is Diagnosed?
Careful people may detect varicocele from irregularity, swelling, or pain in the testicle during self-exam. In patients with complaints of infertility, the diagnosis of this disease is usually made during the doctor’s examination. Moreover; Pain experienced after sexual activities such as standing for a long time, doing sports or exerting effort may be a symptom of varicocele. This examination is done as part of the genital examination.
The patient should be examined in a standing position at room temperature of 21 -22 degrees. The testicles and genital area are observed while the patient is standing and standing upright. The patient is visually and manually controlled both in the normal position and by performing straining maneuvers.
It should be determined whether there is expansion in the vascular structure with normal and straining maneuvers. With these procedures, the presence of varicocele is clinically established. The gold standard in diagnosis is a doctor’s examination. In addition, Scrotal Doppler ultrasonography is performed to support the clinical diagnosis, to determine the degree of varicocele and to decide on surgery.
How is Treatment?
After the diagnosis of varicocele, first of all, it should be checked whether there is a difference in testicular dimensions and the consistency of the testis.
Semen analysis, in which sperm parameters are evaluated, is decisive in the treatment. If there is no problem in the sperm parameters of the patient, it is controversial whether to operate or not.
Such patients may impair sperm parameters;
- Eating habits
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Exposure to toxic substances
Antioxidant drugs and nutritional methods can be recommended to improve sperm parameters and the environment where sperm are found. After the diagnosis, the question of which varicocele patients should be operated comes to the fore. It is not the right approach to decide on surgery by looking at the degree of varicocele. In some cases, even 1st degree (Grade 1) varicocele can be operated, while in some cases surgery decision may not be made for 3rd degree (Grade 3) varicocele. The decision of surgery is a situation that varies according to the patient.
Supportive treatments can be offered to patients who are diagnosed but do not have infertility problems or have borderline sperm parameters. Antioxidant agents can be given to patients who have not experienced severe sperm loss, whose sperm motility has not completely disappeared, and whose sperm deformity is minimal. However, surgery may be recommended for patients diagnosed with impaired sperm parameters and infertility. Exercise, dietary changes, and lifestyle changes are not helpful in relieving discomfort in such patients.
As a result;
- A patient with normal sperm parameters, only radiological varicocele, no reflux or a vessel diameter below normal does not need to be operated.
- Cases with impaired sperm parameters benefit more from surgery.
- Clinical follow-up by evaluating testicular size and consistency is important in adult varicoceles.
- Varicocele surgery is not a correct approach just because of pain.
- After the operation, 60-70% improvement in sperm parameters occurs.
- It is important to perform the postoperative evaluation at the 6th month and to determine the changes in sperm parameters.
- The accepted approach in treatment is interventions made from the inguinal region by microsurgical method.
Frequently Asked Questions About
How is Varicocele Pain?
Varicocele pain is an annoying blunt pain in the testis that manifests itself. This pain can be felt in the groin area and testis, but it can also spread to the leg from time to time. Varicocele pain can be relieved with painkillers. The pain experienced can be confused with different ailments.
In addition to the presence of varicocele in a patient who presented with testicular pain;
- Hernia
- Urinary tract or urinary system stones (kidney stones) that have fallen into the bladder
- Orchitis, testicular infection
- It should be evaluated whether the vascular structure of the testis rotates around itself and causes blood flow.
The pain caused by such ailments can be confused with varicocele pain. A number of inquiries such as whether the person has complaints during urination, whether the swelling in the testis increases, whether the pain starts suddenly, and laboratory methods can provide the differential diagnosis.
Not every pain experienced has to be a varicocele. The pain may be felt more prominently after standing for a long time, walking, exercise, and sexual activity.
How is the Testicle Appearance in Varicocele?
Varicocele does not make any changes in the testis. However, in advanced home varicocele patients, the veins in the testicles become superficial, just like varicose veins in the legs. Varicose enlarged veins are palpable on the skin and give an image.
In Who Is Varicocele More Seen?
The cause of varicocele is unknown.
However, there are some risk groups:
- More obese people
- People who do high-weight sports that increase intra-abdominal pressure
- Those who have chronic asthma and chronic coughing attacks
- Those who experience chronic constipation that increases intra-abdominal pressure
- It can be evaluated as an occupational disease as in varicose disease. It is more common in professions that require standing, such as teachers and police.
Varicocele is frequently seen in people who have varicose veins in the legs because they have vein disease. Conversely, varicose veins are common in people with varicocele.
Since the two diseases are connected to the veins, the insufficiency of the valves in these veins may occur due to factors such as problems in the conduction of blood.
What is Bilateral Varicocele?
While varicocele is seen in 90% left testis, it can be seen bilaterally in 8-9%. The bilateral appearance of varicocele is called bilateral.
Are There Any Foods That Are Good For Varicocele?
Nutrition has nothing to do with the formation or treatment of varicocele. Only people with chronic constipation can be evaluated in this group. Constipation-solving fiber or olive oil diet can indirectly benefit indirectly.
Does It Cause Infertility?
Varicocele is one of the most treatable causes of infertility. If varicocele causes male infertility, then surgery can be decided. However, it should be taken into account that not every varicocele is a cause of infertility and that sperm values may not improve in every patient after surgery.
Does Varicocele Prevent Erectile Dysfunction?
The testis has two main functions. Varicocele can cause dysfunction in the sperm and hormone-producing testicles. Chronic varicocele can cause a decrease in testicular size in the future, resulting in a decrease in sperm production as well as a decrease in the production of the male hormone called testosterone. If chronic varicocele is not treated, it can cause low testosterone and loss of erection and sexual desire.
What are The Degrees?
According to the examination performed in the clinical setting, varicocele is evaluated as 3 stages, namely Grade.
1st Degree (Grade 1) :
It is the situation in which the patient who is examined in outpatient has no symptoms and a varicocele is detected manually when straining.
2nd Degree (Grade 2):
A mild varicocele is seen in the standing eye. It is the situation in which the veins become clearly visible by hand as a result of the pushing maneuver.
3rd Degree (Grade 3):
It is the situation in which the veins are visible without pushing the patient in the standing examination, and this image becomes more evident at the end of the pushing maneuver.
For Which Patients Is Varicocele Surgery Decision Made?
In order to decide on varicocele surgery, it is necessary to reveal the presence of varicocele in the examination and to have infertility problem in the patient.
In patients with this condition, surgery can be decided with the support of the following criteria:
- Reduction in testis size, softening in testis consistency
- 3 mm of vascular dilatation with Doppler Ultrasonography. to be on it.
- Determination of blood reflux in Doppler examination
- Deterioration of sperm parameters in semen analysis
Addition, varicocele treatment can be recommended as a risk factor before a new application, if it is known that this failure occurs due to the sperm factor, in patients who have had a varicocele but have previously applied but failed. It is not correct to decide on surgery for people who only experience testicular pain.
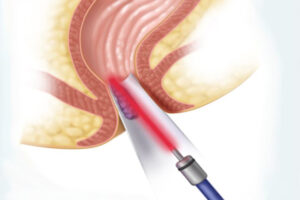
How is Varicocele Surgery Performed?
Varicocele surgery is performed by microsurgical method. The testis veins are reached by entering through a 2 cm incision in the inguinal region. Under the microscope, the enlarged veins are separated from other veins and ligated.
How Long Does the Surgery Take?
Since varicocele surgery is performed with microsurgical methods, all the veins in that area must be ligated. Depending on whether the operation is unilateral or bilateral and the number of vessels connected, the duration may vary between 1-2.5 hours.
Are There Risks of Varicocele Surgery?
Since varicocele surgery is performed by microsurgical method, the complication rate is extremely low. The most important risk is the ligation of the testicular artery and the resultant shrinkage of the testicle and impaired blood supply after the operation.
However, since the operation is performed by microsurgery, the separation of arteries and veins can be made very clearly. The probability of experiencing such a complication is extremely low today. The possibility of hydrocele, that is, fluid collection around the testicles, is also extremely reduced.
Apart from this, risks such as the development of post-operative infection and bleeding that can be experienced in all surgeries should not be ignored. Possible problems are minimized with precautions such as paying attention to sterilization and controlling bleeding.
Are There Different Treatment Methods For This Disease?
Varicocele is treated with different surgical and radiological methods.
Varicocele embolization; By entering from the groin with interventional radiology methods, occlusive material can be injected into the enlarged veins.
However, in this method, side effects such as mobilization of the occlusive substance, that is, going to other places, loss of effectiveness of the substance over time, pain and allergic reaction may be experienced. This treatment approach is not highly recommended in international guidelines.
There are surgical methods used other than microsurgery. There are inguinal, high inguinal or laparoscopic approaches. However, surgery performed under the microscope from the lower inguinal region is considered the gold standard.
Does Varicocele Recur?
There are different treatment methods for varicocele, but the probability of recurrence in surgeries performed with microsurgery is almost zero.
How Long Is the Recovery Time of Varicocele?
After the operation performed with the microsurgery method, the patient can return to his normal activities within 2-3 days and to his routine business life within 1 week and 10 days. Performing activities that require heavy effort, such as exercise, may take 4-6 weeks.
When Do Sperm Fix After Varicocele Surgery?
Sperm production time should be considered in order to evaluate the effect of varicocele surgery on sperm. The average time from the main germ cell to the production of mature sperm in the testis is considered to be 90 days.
Therefore, sperm parameters are checked every 3 months after the operation. The best improvement in sperm production after varicocele occurs in the 6th month. If there is an improvement in sperm parameters in the 6th month, the 9th and 12th months should be waited when the increase becomes more pronounced. However, if there is no change in sperm parameters 6 months after the surgery, no additional recovery due to surgery should be expected in the patient.
It is necessary to direct the patient to other treatment alternatives. After the surgery, 60-70% of the patient’s sperm parameters improve.
While there is no improvement in 30-40% of patients, less than 1% of patients may experience worsening after surgery. This very rare condition occurs mostly in patients with bilateral varicocele.
What Are The Conditions That Patients Should Pay Attention To After The Surgery?
In the early period after varicocele surgery, it is necessary to stay away from sports activities, jobs that require heavy exercise, and sexual activity by following the doctor’s recommendation. It is appropriate to wait 15-20 days for sexual activity and 4-6 weeks for sports and other exercises that require effort. Apart from these, it is necessary to follow the treatment methods recommended by the doctor.
Is There Any Pain In The Ovary After The Surgery?
In varicocele surgery, which is a surgical intervention, there may be some pain in the form of neuralgia, especially due to the damage to the nerve tissues in the testicular region.
In addition, it is not a correct approach to operate only on patients with testicular pain complaints. There may be many underlying causes of pain in such patients.
In such patients, pain continues after surgery. The most important reason for unsuccessful surgery is not infertility, but patients who experience pain alone.
Is There Swelling After Varicocele Surgery?
After the operation, testicular prolapse on the operated side due to the release of the testicular connective tissue can be considered normal. However, swelling is the increase in the normal fluid around the testicle, that is, the development of Hydrocele.
It is a situation that is more common in methods applied other than microsurgery. It is a problem seen in less than 1% of surgeries performed with microsurgery method.
Since the lymphatic vessels are clearly revealed and procedures such as ligation or burning are not performed, the lymphatic circulation is not affected.
Do Those Who Have This Surgery Have Children?
After the surgery, 60-70% of the patients have an improvement in sperm parameters. If there is no improvement in sperm parameters in the 6th month, it is useful to direct the patient to methods such as vaccination or in vitro fertilization, considering the age factor and female factor according to the sperm parameters of the patient.
If a young patient who comes to the doctor to evaluate the general condition and is diagnosed with varicocele with impaired sperm parameters, if he wants to have a child in normal ways, varicocele surgery can be recommended for such patients.
However, it is more appropriate to direct patients with the same diagnosis and older age to treatments such as in vitro fertilization or vaccination, instead of wasting time with varicocele surgery. Here, the age and clinical condition of the patients are taken into consideration. Infertility should be evaluated bilaterally, not only as a situation of the individual but also as the situation of the couples.
What Happens If Varicocele Is Not Treated?
Varicocele is a chronic condition and does not resolve itself. If left untreated, it may progress to decrease in testicular size, enlargement of varicocele, further decrease in sperm parameters, and hormonal disruptions in the testis in the future. It is none of these and can remain as a standard for the person for life. There is no such thing as surgery for every varicocele.
Does Varicocele Occur in Teens and Children?
Another important problem of varicocele is its monitoring in young people. Varicocele is seen less than 1% in the pediatric age group. In the 13-15 age group, it is seen at a rate of 15%.
It is very difficult to evaluate the effect of varicocele, which occurs in the 16-17 age group, on the testis. It is not very healthy to evaluate sperm function because sperm production has not started completely in this age group. In addition, it is not ethically correct to have a semen analysis performed by young people in this age range.
In young people who have difficulty in making a decision about surgery; While evaluating testicular dimensions and testicular consistency, the degree of varicocele should be determined radiologically. And if it causes difference and reduction in testicular size, surgery may be considered.
However, clinical follow-up of varicocele is more appropriate in young people who do not differ in testicular size and consistency, at least when they reach puberty, by evaluating sperm parameters by semen analysis and deciding for surgery.