What is Tympanoplasty?
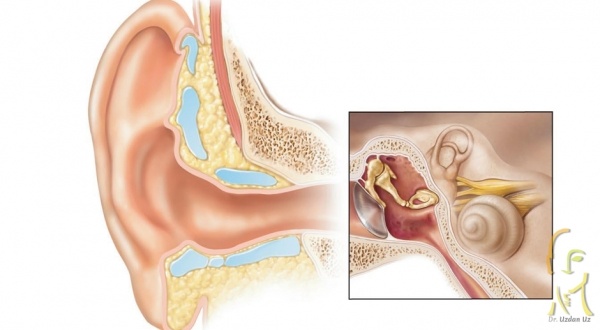
Tympanoplasty surgery is technically the repair of the eardrum and the auditory system in the middle ear, and the removal of inflammation in the mastoid bone in the middle ear and behind the ear.
Depending on the extent of the disease detected in the patient, the operation can only be performed by repairing the hole in the eardrum (myringoplasty) and repairing the ossicular system in the middle ear with membrane repair (tympanoplasty), clearing the inflammation that has progressed into the mastoid bone (mastoidectomy) or a combination of these operations are performed together with.
In tympanoplasty surgery, the perforated eardrum is closed and the ossicles that provide sound transmission are repaired with the help of auxiliary operations. Necessary tissue, cartilage, bone fragments or artificial prostheses created for the middle ear are used.
What Causes Eardrum Perforation?
The eardrum is a thin membrane in the ear canal that separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear. Perforation of the eardrum occurs as a result of rupture or perforation of this thin membrane. When the eardrum is perforated, hearing is reduced and sometimes there is discharge from the ear. With the tearing, a buzzing and ringing sound may be felt in the ears, but usually no pain occurs. A common problem is perforation of the eardrum, which can happen suddenly after a thunder-like sensation.
We can list the situations that can cause perforation of the eardrum as follows:
- Scuba diving
- Airplane trip
- Exposure to shock waves
- Driving at high altitudes
- Injury and trauma
- Sudden pressure changes
- Insertion of foreign objects into the ear
- Otitis media
- Getting hot or acidic liquids into the ear canals
- Car accidents
- Sports injuries
- Falling on the ear
- A hard blow to the ear
- Explosion near the ear
What Are The Symptoms?
We can list the symptoms of eardrum perforation as follows:
- Sudden and sharp ear pain in the ear,
- Bloody, clear or pus-like discharge from the ear,
- Ringing or buzzing in the ear,
- Onset of hearing loss,
Diagnosing Eardrum Tear
If there is a lot of discharge in the ear, the doctor first cleans the ear canal.
Otoscopic Examination:
The inside of the ear is looked at with a lighted instrument called an otoscope. If there is a hole or tear in the ear, this can be seen during the examination.
Audiometry Test:
Audiometry test may be requested to measure hearing. In this test, the patient listens to sounds at different frequencies with the help of headphones and presses the button in his hand every time he hears the sounds.
Eardrum Perforation Treatment
Most hearing loss due to damage to the eardrum is temporary and hearing returns to normal after the damage has healed.
There is no cure for people whose hearing loss is not temporary. The goal of treatment is to prevent further damage to the ear.
Antibiotics may be needed to treat or prevent an ear infection. If the puncture is causing pain, painkillers can also be used.
Eardrum Perforation Surgery
“Tympanoplasty” surgery applied in eardrum perforations is technically the process of repairing the eardrum and the auditory system in the middle ear. In the surgery, inflammation in the mastoid bone is also cleaned.
Depending on the extent of the disease, the operation can be performed only by repairing the hole in the eardrum, clearing the inflammation that has progressed into the mastoid bone, repairing the ossicular system that provides sound transmission in the middle ear with membrane repair, or a combination of these surgeries.
What Should Be Considered After the Surgery?
You are usually discharged the day after your tympanoplasty surgery, after your dressing is done.
The points you should pay attention to after the operation are as follows;
- To protect your ear from infection after surgery, you should stay away from water for a while.
- You should regularly use the antibiotic and cortisone-containing drops given by your doctor.
- It is not recommended to travel by plane in the first month.
- You should protect your ear from every impact.
- It is recommended to sleep with your pillow elevated for the first week after the operation. (To reduce blood pressure and edema in the middle ear and behind the ear).
- Do not cover your mouth when sneezing.
- Since constipation can adversely affect the ears due to straining, prevent this ailment by consuming fibrous foods and drinking plenty of water.
- You should not do sports such as diving, swimming and water skiing for 8 weeks after the operation. Avoid heavy exercises.
- The tampons in the external ear canal should be replaced by the doctor. Do not remove tampons without consulting a doctor.
Disadvantages of Perforation of the EarDrum
The eardrum has two main roles:
-
Hearing:
When sound waves hit, it makes the eardrum vibrate. The middle and inner ears convert sound waves into signals. The auditory nerves transmit these signals to the brain and hearing takes place.
-
Protection:
The eardrum is also a barrier that protects the middle ear from water, bacteria and other foreign substances.
Some problems may arise, especially if the tear in the eardrum has not healed on its own within three to six months.
For example:
Hearing Loss:
Usually temporary, but lasts until the tear or hole in the eardrum heals. The size and location of the tear can affect the degree of hearing loss.
Middle Ear Infection:
An unhealed tear in the eardrum can cause (recurrent or chronic) infections. As a result, discharge and hearing loss may occur.
Middle Ear Cyst (Cholesteatoma):
Consisting of skin cells and other debris, this cyst is very rare. Normally, ear canal debris goes to the outer ear along with earwax.
However, in the perforation of the eardrum, skin rash may escape into the middle ear and cause cyst formation.
What Should Be Done To Prevent Eardrum Ruptures?
- If you have an ear infection, be sure to get treatment.
- Do not insert foreign objects into your ear. Never try to remove hardened earwax with objects such as cotton swabs, paper clips or hairpins.
- Use cotton buds with care.
- Protect your ears during airplane travel. If possible, do not fly until you recover if you have a cold or an active allergy that causes nasal or ear congestion. On takeoffs and landings, keep your ears open with pressure-equalizing earplugs, stretching or gum.
- Do not be exposed to very loud noise.
- Avoid heavy sports exercises or do them in a controlled manner.
- Avoid getting hot water and acidic water into your ear.
- Consult a doctor if your ear has been hit or hurt.