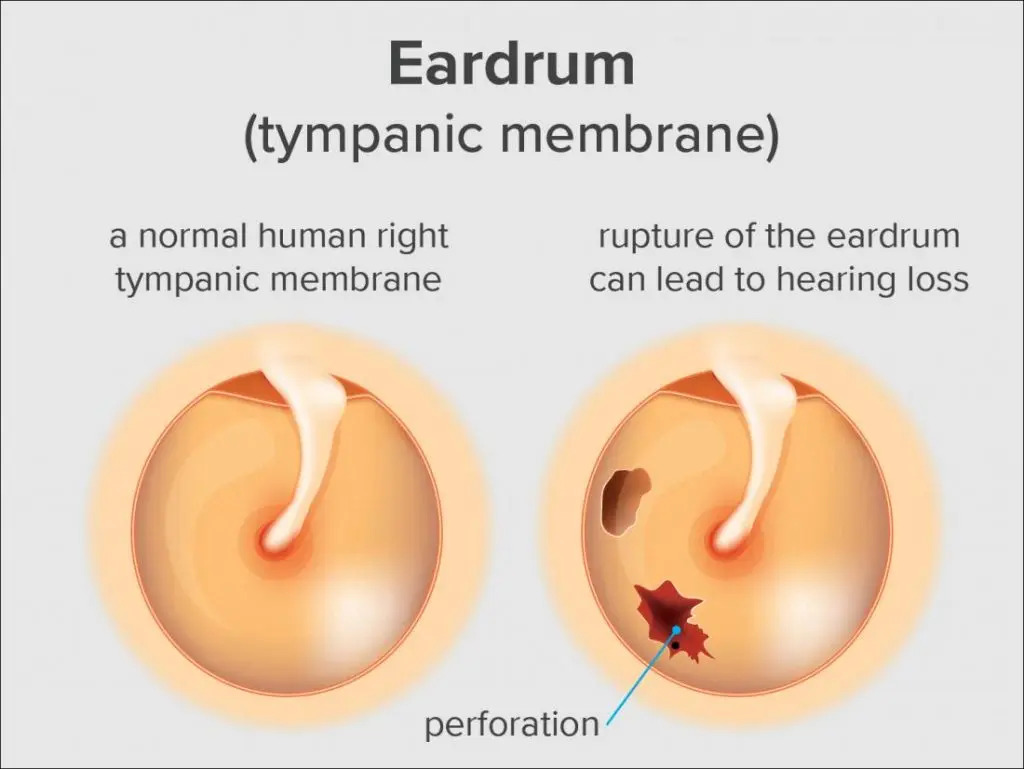
The Tympanic Membrane is a vital component of the human ear and is more commonly known as the eardrum. It is a thin, circular layer of tissue that marks the point between the middle ear and the outer ear. It has a thickness of about 0.1 mm, a diameter of 8 to 10 mm, and a mass weight of 14 mg. Despite this small size and mass, the eardrum is extremely rigid and flexible.
The function of the eardrum is to assist human hearing. When sound waves enter the ear, they hit the eardrum. The membrane (eardrum) vibrates with the force of the sound wave and transmits the vibrations further inwards, to the bones of the middle ear.
Patients with ruptured or absent eardrums have extreme difficulty in hearing and experience complete hearing loss over time.
A Ruptured Eardrum occurs as a result of a tear in the thin membrane that separates your outer ear from your inner ear. When the membrane ruptures, this condition causes severe pain in the ear in some people, while in others it goes away on its own (without treatment) within a few months with no symptoms.
The eardrum senses and vibrates when sound waves enter the ear. It then converts these sounds into nerve impulses that transmit to the brain. It also protects the middle ear from water, bacteria and foreign bodies. If damaged, bacteria can enter the middle ear and cause a middle ear infection or damage your hearing.
One of the most common causes of ruptured eardrum is an ear infection. When the middle ear becomes infected, fluids build up behind the eardrum and put pressure on the eardrum. When the pressure increases, the eardrum may rupture.
The eardrum sometimes ruptures as a result of what is known as barotrauma. Barotrauma occurs when the pressure outside the ear is drastically different from the pressure inside the ear, meaning the two pressures are unequal. The following causes can cause barotrauma:
You can also tear your eardrum due to a severe blow to your ear. Any blow to the ear or the side of your head can cause a tear.
Although pain is the main symptom of ruptured eardrums, some people do not notice any pain or symptoms when their eardrum is ruptured.
Those who feel the pain see that the affected ear begins to flow after the pain has passed. At this point, the eardrum ruptures. If the rupture is caused by a middle ear infection, it usually causes bleeding.
Most of the patients do not care about the symptoms caused by the perforation of the eardrum. Even if the discharge in the ear continues for years, some patients do not take this into account. Conducting such behaviors paves the way for further progression of the disease and the emergence of larger health problems.
Perforation of the eardrum due to impacts may heal spontaneously if it does not cause an infection. However, if the treatment is desired to progress quickly, people with symptoms should definitely see a specialist doctor. Because these conditions can only be diagnosed by doctors. As specialist doctors, otolaryngologists should be preferred. Otolaryngologists listen to patients’ complaints and apply some hands-on hearing tests. As a result of these tests, diagnoses are made about the condition of the ear.
Treatments for ruptured eardrums serve to relieve pain and eliminate infection. The vast majority of ruptured eardrums heal within three months.
But if the healing of the eardrum is slow, the following methods can be applied:
If your ear takes a long time to heal, your doctor may cover the eardrum with a patch. Patching the eardrum is done by placing a medicated paper patch over the tear in the eardrum.
To prevent an ear infection or treat an existing infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. If the ruptured eardrum is causing pain, the doctor may recommend using an over-the-counter pain reliever.
In some cases, surgery may be required to close the hole in the eardrum. The surgery is usually done as an outpatient procedure and takes several hours. During surgery, your doctor takes tissue from another part of your body and attaches it to the eardrum.
While your eardrum is healing, you must take care to keep your ear dry. Until your doctor says your eardrum is healed, you should not swim, use a shower cap or water-repellent earplugs while showering.
Ear infections are the most common cause of eardrum ruptures in children. Since 5 out of 6 children will have had at least one ear infection by the age of 3, it is a good idea to take your child to the doctor immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms:
Because children’s eardrums are more sensitive than adults, the damage can have long-term effects on hearing if left untreated.
Eardrum surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia. It can be applied with different techniques. The surgery can be performed behind the ear or through the ear. However, in order for it to be done through the ear, the hole must be small or the ear canal must be of appropriate width.
The tissue (patch) placed to close the hole can be ear cartilage, the membrane surrounding the cartilage, both, or the membrane of the chewing muscle behind the ear.
It takes about 2-3 weeks for the patch to fuse and integrate with the eardrum. Eardrum surgery is an operation that usually results in success. However, if the hole does not close, it may need to be repeated.
Hearing recovery takes an average of 2-3 months. At least 6 weeks should be waited to comment on the hearing.
There are some points that the patient should pay attention to after eardrum surgery.
These;
What is Varicocele? Varicocele is the varicose veins that drain the blood in the testicles,…
What is Hemorrhoids ? It is a disease caused by the loosening of the veins…
What Is Monkeypox Virus? Symptoms and Ways of Transmission! The monkeypox virus, which has been…
What is Pelvic Venous Congestion Syndrome? (Failures Observed in Ovarian/Testicular Veins) What is Pelvic Venous…
What is Myoma ? Myoma, is a benign tumor arising from the uterine muscles. It…
What is Back Lift? Back stretching, excessive weight gain and aging may cause you to…