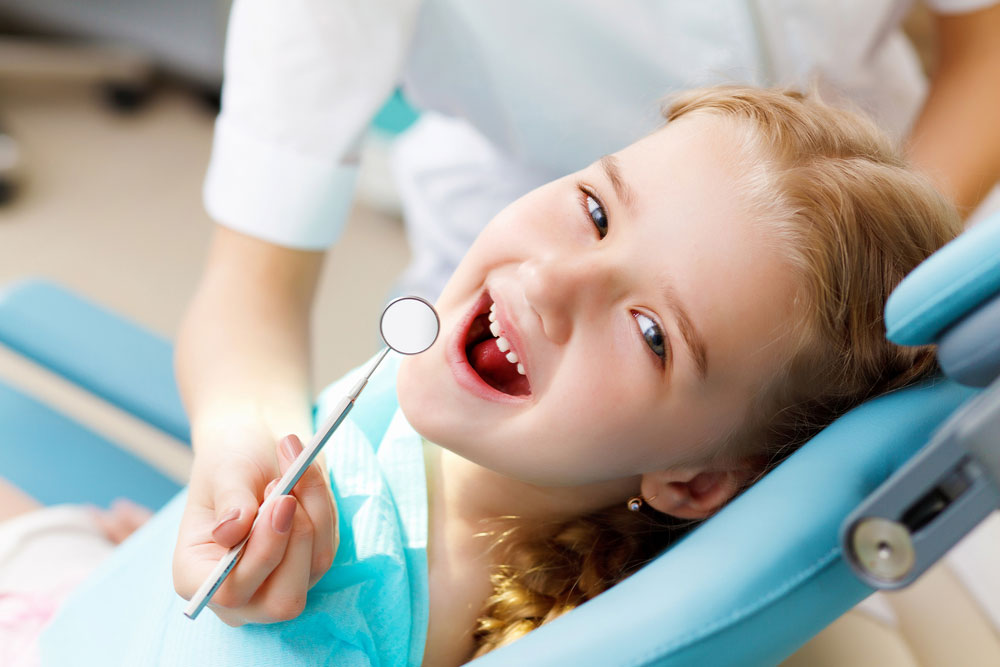
What is Pedodontics (Pediatric Dentistry)?
What is Pedodontics?
Pedodontics (Pediatric Dentistry) is a department that aims to protect the milk and permanent teeth of 0-13 age group children in a healthy way, and to eliminate the problems caused by caries, trauma, hereditary and similar factors in these teeth.
Pedodontics is a branch of dentistry that follows and treats the oral-dental health and maxillofacial development of children from infancy, and also includes preventive measures.
In this period, pedodontists perform all kinds of preventive and curative treatments and preventive applications according to the oral and dental health needs of babies, children and young people.
- Oral and Dental Care and Nutrition Recommendations
- Child Prostheses
- Tooth extraction
- Preventive and Preventive Practices Against Caries; Fluoride Gel, Fluoride Varnish, Fissure Sealant
- Treatment of Dental Traumas
- Endodontic Treatments (Canal Treatments, Amputations)
- Treatments to Stop Bad Mouth Habits (Finger Sucking, Nail Biting, Lip Biting, etc.)
- Restorative Treatments (Fillings) in Milk and Young Permanent Teeth
- Placeholders
Why Are Milk Teeth Important?
There are 20 milk teeth in total. The most important task of milk teeth is to provide nutrition to the child. In addition, the proper development of speech also depends on the presence of milk teeth.
Milk teeth protect the area they cover for the permanent tooth that will replace them and guide it while the permanent tooth is erupting. When the primary tooth is pulled out early, this natural place-holding function also disappears.
What Are Protective Practices?
The primary aim of pediatric dentistry is to take measures to prevent dental problems and to direct children to a caries-free future. The procedures applied for this purpose are called Preventive Dentistry Practices.
In preventive practices for the prevention of caries, great importance is attached to educating the child and his family about oral and dental health and nutrition.
Preventive dentistry applications include superficial fluoride and fissure sealant procedures.
What Do Fissure Sealers Do?
It is a fluid filling material that closes the deep and decay-prone fissures (grooves) on the chewing surfaces of permanent teeth and does not allow bacteria to reach there, thus preventing caries.
Dental vaccination should be checked every 6 months.
What is Fluorine Application?
Fluorine is an element that prevents tooth decay and strengthens the structure of teeth.
Since the enamel is not fully mature when the teeth first erupt, newly erupted teeth are generally less resistant to caries and are prone to caries formation.
Fluoride strengthens the enamel, protects the tooth against acid attacks and thus helps prevent the formation of dental caries.
Professional superficial fluoride application is a protective method that can only be applied by dentists.
Superficial fluor should be applied by a dentist every 6 months.