Beware if your child repeats sentences!
(Accumulation of fluid in the middle ear?)
Accumulation of fluid in the middle ear is one of the most common diseases in the pediatric age group and makes families uneasy. Its a disease that can cause children to watch television loudly, repeat sentences, failure at school, and permanent hearing loss when left untreated.
What is known as fluid accumulation in the middle ear is called serous otitis media or otitis media with effusion. The problem; It occurs as a build-up of fluid in the middle ear cavity, behind the eardrum, without inflammatory symptoms such as ear pain, fever, and redness of the eardrum.
Accumulated fluid is not an external fluid or inflammation into the middle ear. The secretion of the middle ear secretion, which should flow from the middle ear to the nasal tube through the eustachian tube, accumulates in the middle ear as a result of obstruction of the eustachian tube, and the disease, which is more commonly seen in the pediatric age group, may also occur in adults.
Frequently asked questions about the fluid accumulation problem in the middle ear in children, which make families uneasy, are as follows.
What causes fluid accumulation in the middle ear?
- Upper respiratory tract infections.
- Factors causing obstruction in the Eustachian tube.
- Nasal inflammation.
- Nasal flesh growth.
- Allergic nose.
What are the symptoms?
Since this disease is not an inflammatory condition, it may give less symptoms than inflammatory ear diseases. Therefore, families should be careful in the presence of the following conditions in children and should consult the ear, nose and throat specialist as soon as possible.
- Lack of hearing (watching television aloud, repeating sentences, shouting speech.)
- Don’t play hard with the ear.
- Retarded in talking.
- The teacher told him that the child did not hear.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Detailed medical history and examination is usually sufficient for diagnosis. We also use audiometry and tympanometry tests to help diagnose and determine the degree of hearing loss.
Could you tell us about the treatment of the disease?
The fluid accumulated in the middle ear usually recovers within 2 months. During this period, the patient may be monitored without medication or used with some medications. Ventilation tube is inserted surgically to the ear in cases where it does not improve.
When is ear tubing needed and how is it done?
- Accumulation of middle ear fluid that has not improved over 2-3 months despite follow-up and treatment.
- The development of hearing loss of more than 40 dB.
- In case of collapsing and sticking of the eardrum, we recommend surgical treatment, ie draining the fluid from the ear and inserting the tube.
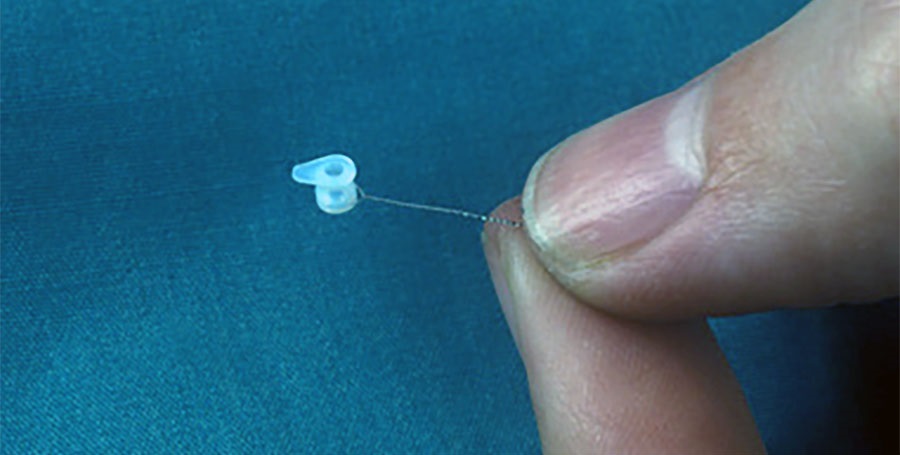
It is a procedure that can be applied under general or local anesthesia for approximately 15 minutes. The procedure is performed under a microscope by making a millimeter incision in the eardrum.
After cleaning the liquid accumulated in the middle ear from this incision, the tube is placed in the previously made incision. If the surgical treatment is rejected in the presence of these symptoms, the patient should know that the patient may develop permanent hearing loss, irreversible changes in the eardrum, and speech disorder.